Published:
This post shows how to setup tensorboard summaries with popular CNN architecture layers in TF. This does not only help debug but also provide insights into working of deep neural nets.
Intro
TF has several wrappers such as keras, tf.contrib.slim etc. This is not to replace them, but some helper function to write code faster in TF only environments and also to fully utilize Tensorboard(from TF-dev summit Feb,2017).
# combine all summaries
summ = tf.summary.merge_all()
# write summaries to file
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(filename)
writer.add_graph(sess.graph) # adds graph too
# when run session
...
...,s = sess.run([..., summ], feed_dict=...)
writer.add_summary(s, count)
Conv Layer
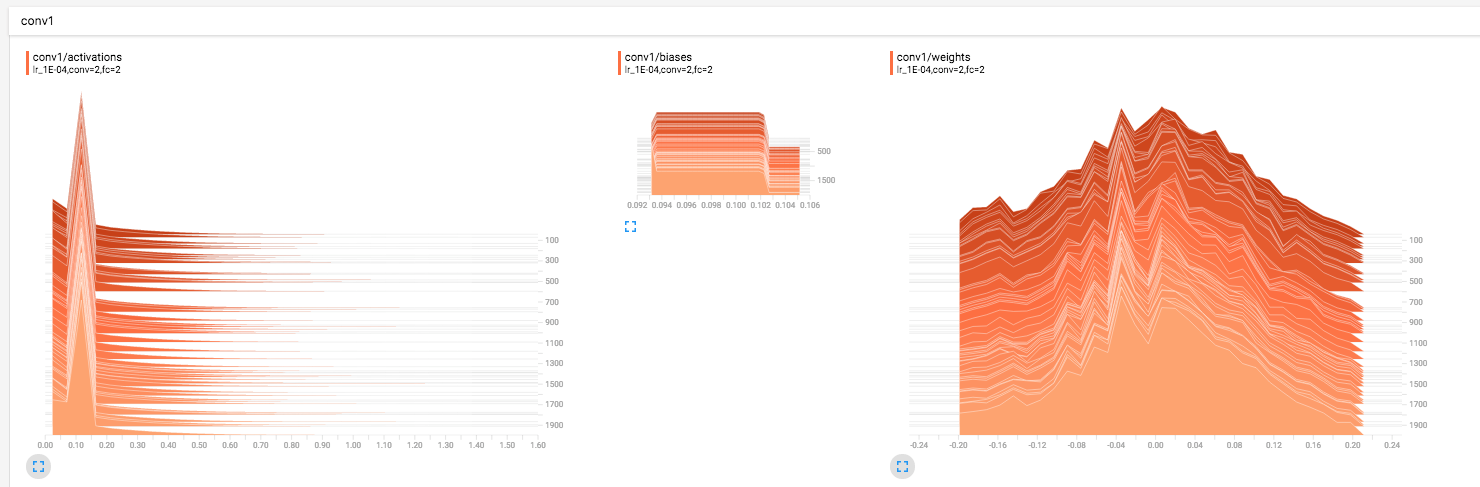
Use this to write a convolution layer with name space. It is very useful for plotting graphs in tensorboard. Modify speciific parameters according to use. This will write summary for weights, biases and activations. These can be visualized using Tensorboard
def conv_layer(input, size_in, size_out,kernel_size,stride=1, layer_name="conv"):
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([kernel_size[0], kernel_size[1], size_in, size_out], stddev=0.1), name="W")
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[size_out]), name="B")
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input, w, strides=[1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME")
act = tf.nn.relu(conv + b)
tf.summary.histogram("weights", w)
tf.summary.histogram("biases", b)
tf.summary.histogram("activations", act)
return act
FC Layer
Fully Connected layer
def fc_layer(input, size_in, size_out, layer_name="fc"):
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([size_in, size_out], stddev=0.1), name="W")
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[size_out]), name="B")
act = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(input, w) + b)
tf.summary.histogram("weights", w)
tf.summary.histogram("biases", b)
tf.summary.histogram("activations", act)
return act
Batch Norm
Batch-Normalization Layer with trainable parameters.
def batch_norm_layer(input,size_out,layer_name = 'bn'):
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
beta = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape = [size_out]),name = 'beta', trainable = True)
gamma = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape = [size_out]),name = 'gamma', trainable = True)
mean, variance = tf.nn.moments(input, [0, 1, 2])
tf.summary.histogram("beta", beta)
tf.summary.histogram("gamma", gamma)
tf.summary.histogram("mean", mean)
tf.summary.histogram("var", variance)
return tf.nn.batch_normalization(input, mean, variance, beta, gamma, variance_epsilon=0.0001, name = 'op')
Deconvolution
This is required in various VAE or GANs style models
def deconv_layer(input, size_in, size_out,kernel_size,stride=1, layer_name="deconv"):
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([kernel_size[0], kernel_size[1], size_in, size_out], stddev=0.1), name="W")
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[size_out]), name="B")
conv = tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(input, w, strides=[1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME")
act = tf.nn.relu(conv + b)
tf.summary.histogram("weights", w)
tf.summary.histogram("biases", b)
tf.summary.histogram("activations", act)
return act
Tensorboard Output

Leave a Comment