Published:
In this post I provide a summary of paper by Zang et al. that won the best paper award at ICLR’17. It is quite informative in terms of understanding why some neural networks can generalize well while others can’t. They provide detailed results to check Generalization Error accross various tests.
Paper : Zhang et al.
Introductions
- Generalization error : Training Error - Test Error.
- Large DNN has small generalization error.
- Generalization is incapable of distinguishing between different neural networks that have actually radically different generalization performance.
- The paper evaluates why some NN are capable of small generalization error while others not.
- Measures to evaluate GE :
- VC Dimension (Vapnik’98)
- Rademacher complexity (Barlett&Mendelson, 2003)
- Uniform Stability(Mukherjee 2003)
Contributions
This paper talks about several inference under following themes
- Randomization Tests
- Role of explicit regularization
- Finite sample expressivity
- Role of Implicit Regularization
Randomization Tests
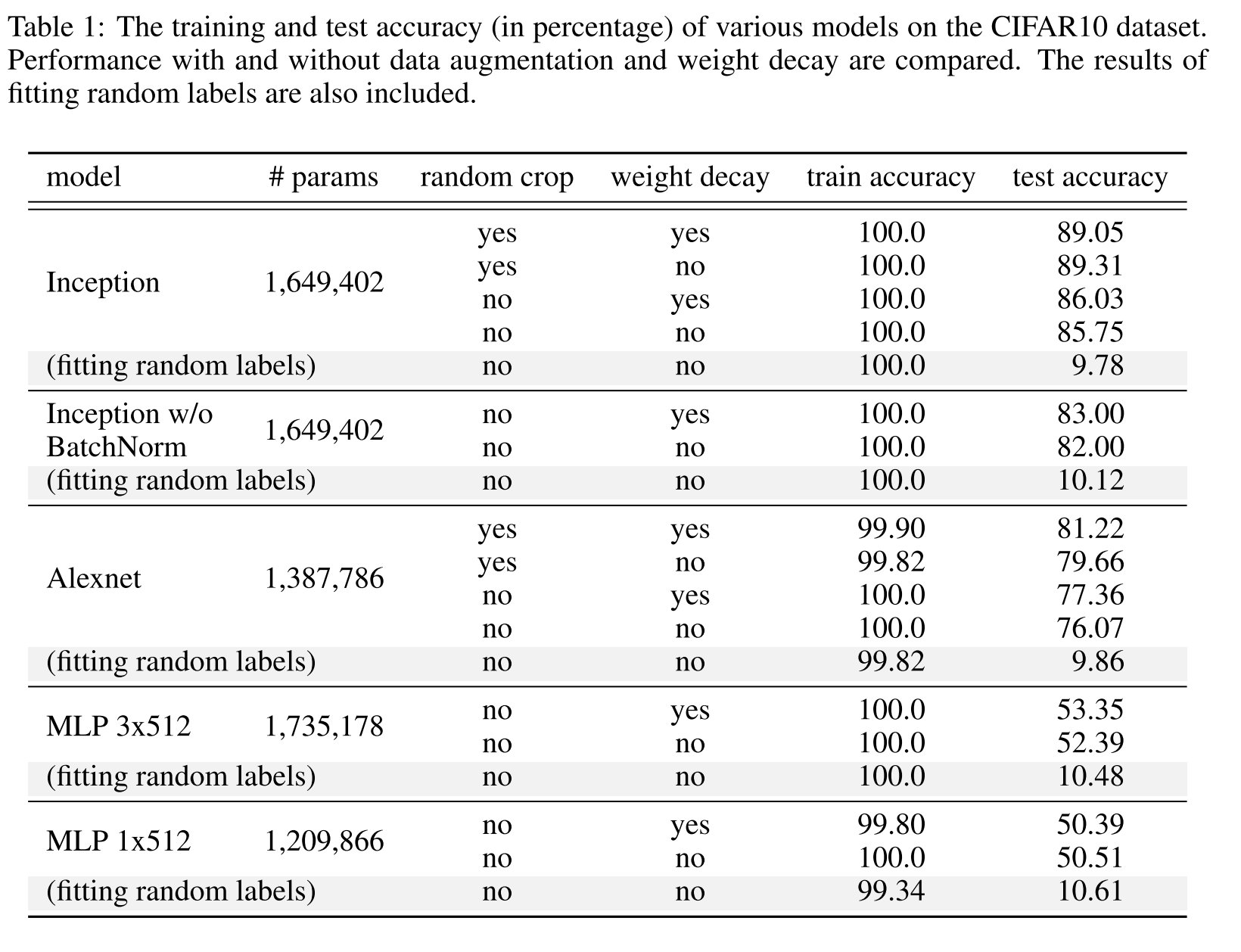
- Deep nn easily fit random labels. By randomizing labels alone we can force the generalization error of a model to jump up considerably without changing the model, it size, hyper parameters or the optimizer. **
- Observations:
- effective capacity is sufficient to learn all dataset.
- Optimization on random label stays easy.
- No significant increase in training time.
- this is similar as data transformation
- Replacing true images with random pixels keeps training accuracy same.
- CNNs can fit random noise
- As noise increases, accuracy steadily decreases. This shows it fits all the parts on images noise and signal.
Role of explicit regularization
- Some of the regularization technique used are weight decay, dropout and data augmentation.
- Explicit Regularization may improve performance but is not sufficient or necessary condition for controlling generalization error.
- This is different from usual convex optimization techniques where regularizer play significant role in convergence.
- Absence of regularizer may not change generalization error.
Finite Sample Expressivity
large neural networks can express any size of training sample, as long as number of parameters are more than $2n+d$ .
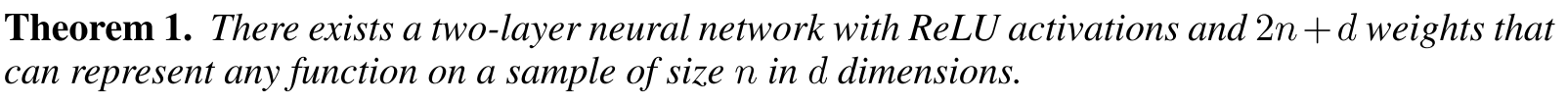
they show that with 2-depth network of sufficient parameter size can learn any training sample.
Role of Implicit Generalization
- Models that has low training error may not have low generalization error.
- In linear models, SGD pays the role of implicit regularizer and always approach to minima within a norm.
- In Deep NN, model trained by SGD still need to be analyzed for their properties.

Leave a Comment