Published:
This blog provides a brief write-up on the paper titled Adversarial Examples Improve Image Recognition. As the paper explains how to use adversarial setting to improve the training of the model for large datasets like ImageNet
Preliminary
Adversarial approach to train a neural network are used to make model robust against adversarial attacks. Previous approaches uses adversarial method in order for the model to defend against them. However, another way could be to use these modifications to improve the accuracy. As an experiment, author trains model on imagenet with adversarial pertubations as explained in [1].
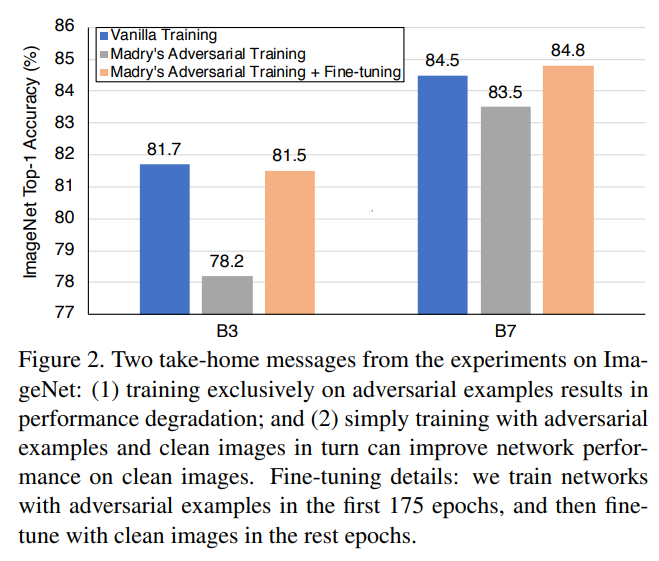
Network trained are not able to provide better performance on clean test data. Even with fine-tuning larger models perform slightly better but smaller models are not performing well. This paper
Adversarial Propagation (AdvProp)
A method that learns from both clean images as well as adversarially modified images. Since clean images are derived from a different distribution as compared to adversarial images, the model needs to also use the batch statistics according to image source. If not, the model may not be effective in extracting accurate features.
In case of data perturbed adversarially, the batch statistics can change due different distributions of the data.
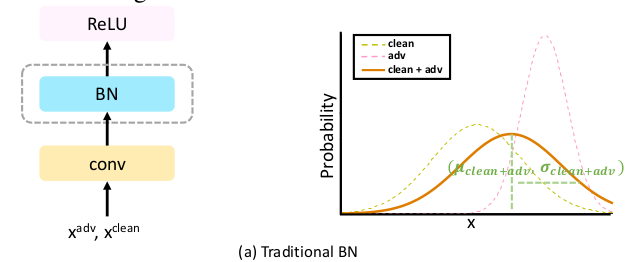
BatchNorm(BN), present widely in modern architectures, captures data statistics by using mean and variance of the input mini-batch. BN for adversarial perturbations may not provide disentangled mean and variance. As an example in the following figure from the paper, right hand graph shows different distributions of clean and adversarial data. But if we use BN in the model as described in the left flow chart the resulting distributions statistics will be the solid line(right plot).
Source: paper:
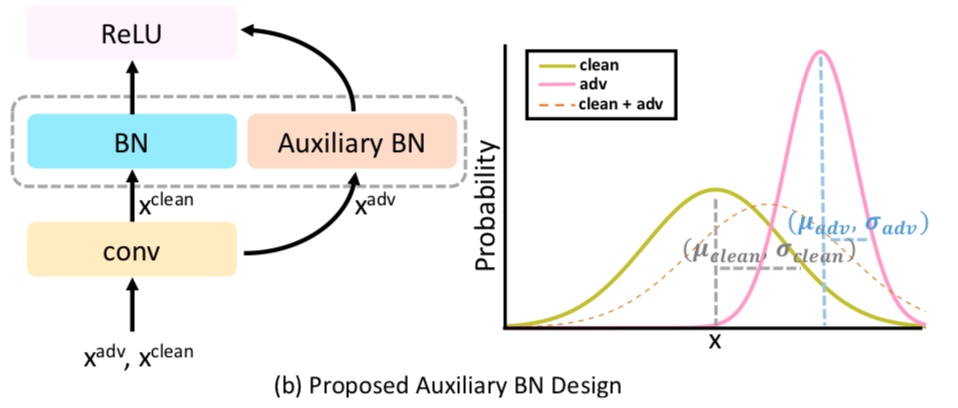
An Auxillary BN can be used to disentangle these distributions and provide individual statistics during training. And during inference, usual primary BN only is used. This is shown in the following figure.
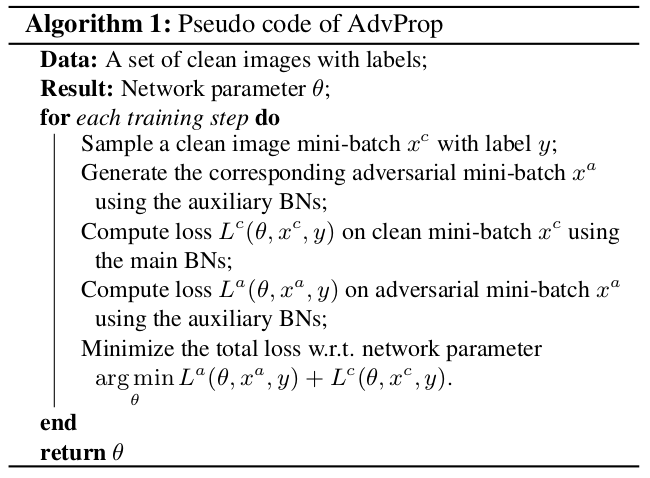
The training of these algo is performed as per the following psuedocode:
Results
Performance of this method results in increase in accuracy of efficient-nets by upto 0.7% on Imagenet dataset
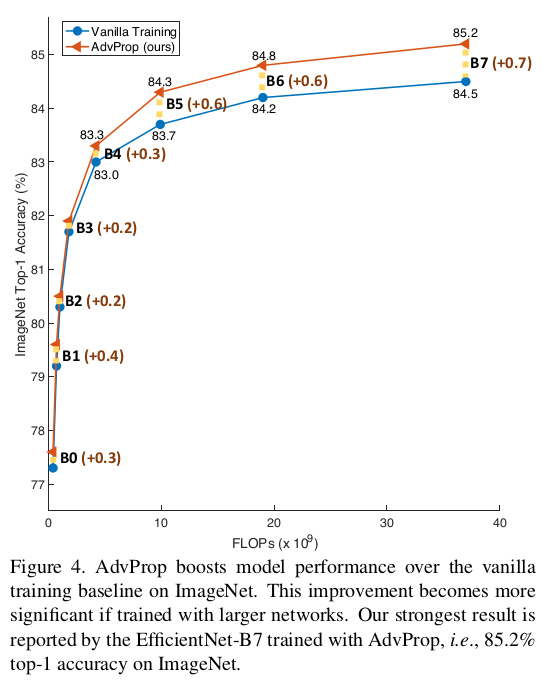
Similarly, comparing the Adversarial propagation wrt Adversarial training(using combined data distribution) of the model, relative improvements of efficientnets is as :
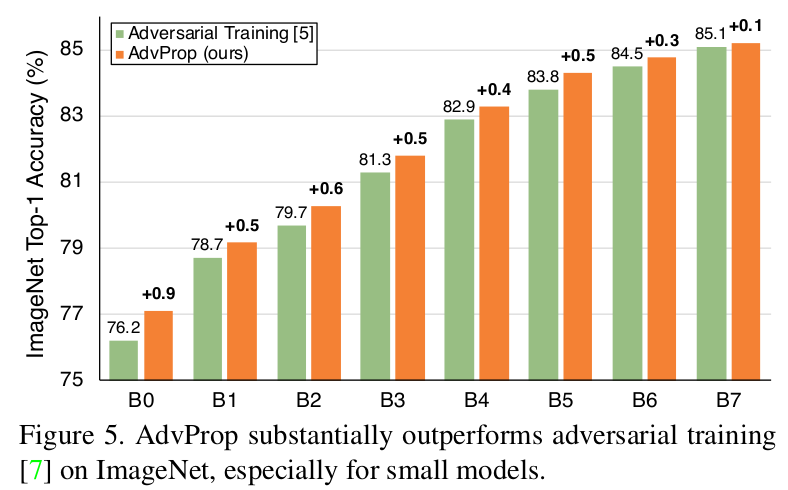
Smaller size efficientnets are shown to perform significantly better than the larger ones, specifically B5 and above.
References :
- Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks: [https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.06083
- Pytorch Code: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models
- Author Code : https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/tree/master/models/official/efficientnet


Leave a Comment